
We introduce the first active learning (AL) framework for high-accuracy instance segmentation of moveable parts from RGB images of real indoor scenes.
As with most human-in-the-loop approaches, the key criterion for success in AL is to minimize human effort while still attaining high performance. To this end, we employ a transformer that utilizes a masked-attention mechanism to supervise the active segmentation. To enhance the network tailored to moveable parts, we introduce a coarse-to-fine AL approach which first uses an object-aware masked attention and then a pose-aware one, leveraging the hierarchical nature of the problem and a correlation between moveable parts and object poses and interaction directions.
Our method achieves close to fully accurate (96% and higher) segmentation results, with semantic labels, on real images, with 82% time saving over manual effort, where the training data consists of only 11.45% annotated real photographs. At last, we contribute a dataset of 2,550 real photographs with annotated moveable parts, demonstrating its superior quality and diversity over the current best alternatives.
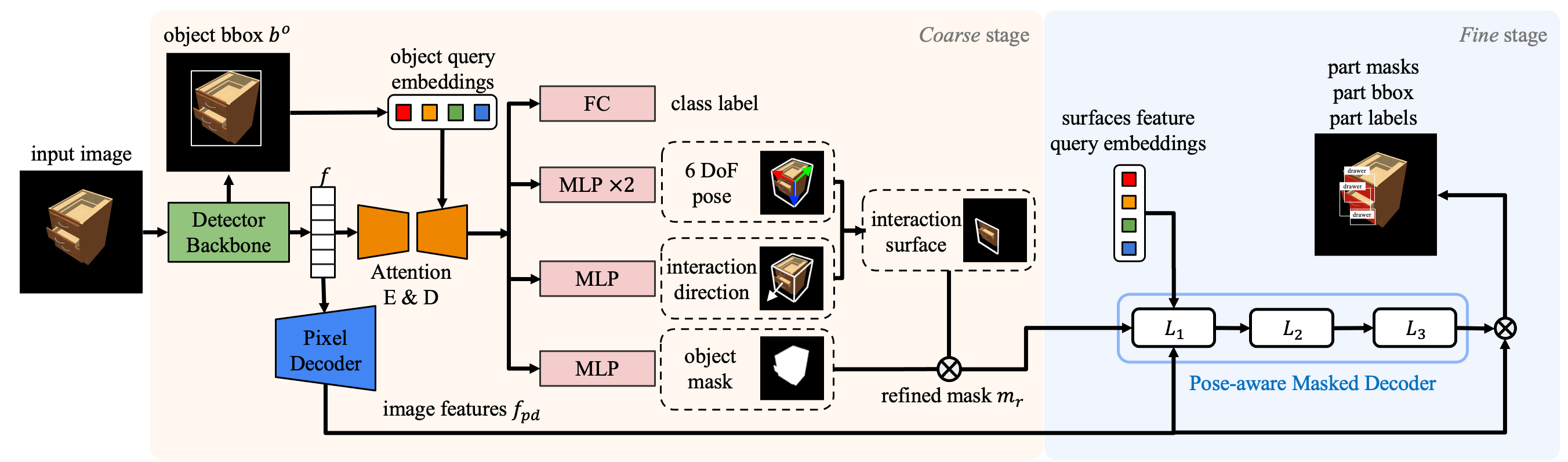
Overview of our pose-aware masked attention network for moveable part segmentation of articulated objects in real scene images.
Utilizing a two-stage framework, we first derive a coarse segmentation by predicting the object mask, its 6 DoF pose, and the interaction direction, subsequently isolating the interaction surface of the objects. In the fine segmentation stage, we combine the object mask and interaction surface to form a refined mask, enabling the extraction of fine-grained instance segmentation of moveable parts.
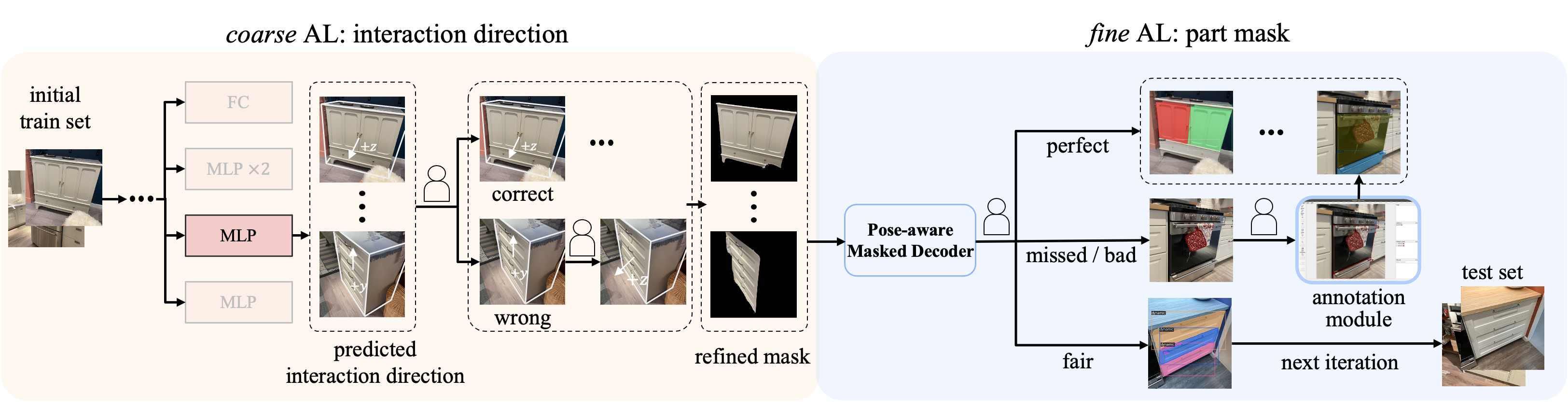
The coarse AL applys on interaction directions and retains high-quality predictions while manually rectifying the rest. These rectified predictions form a constructive prior for refined mask prediction. Subsequently, the fine AL stage utilizes these refined masks, employing an iterative training method with continuous human intervention for accurate part mask annotation.

Our scalable AL model allows us to accurately annotate a dataset of 2,550 real photos of articulated objects in indoor scenes.
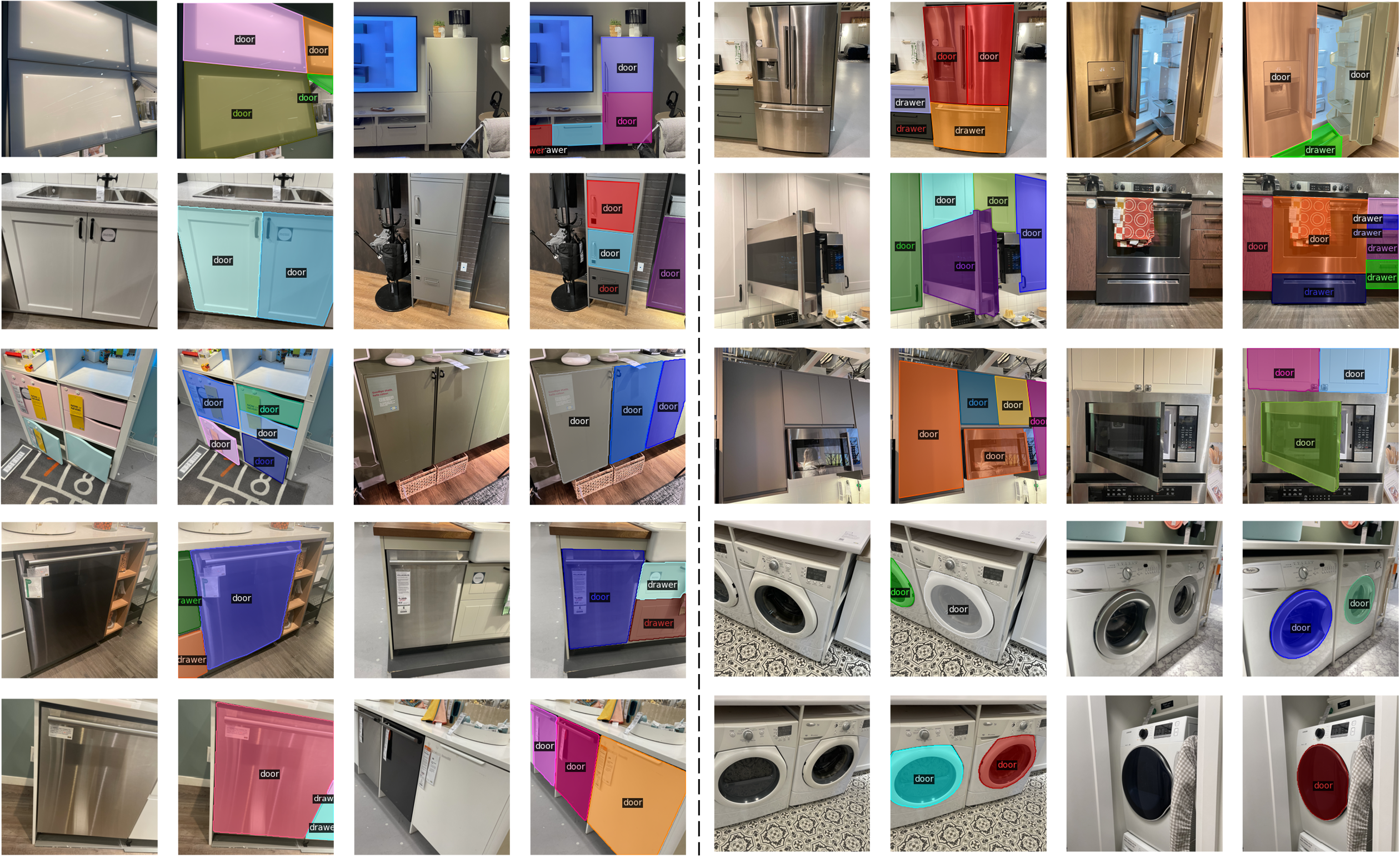
We consider 6 object categories -- Storage, Fridge, Dishwasher, Microwave, Oven and Washer. We organize our dataset according to the primary object depicted in each image. Our dataset includes 333 different articulated objects and 1,161 distinct parts in total, offering a more uniform data distribution across all 6 categories.
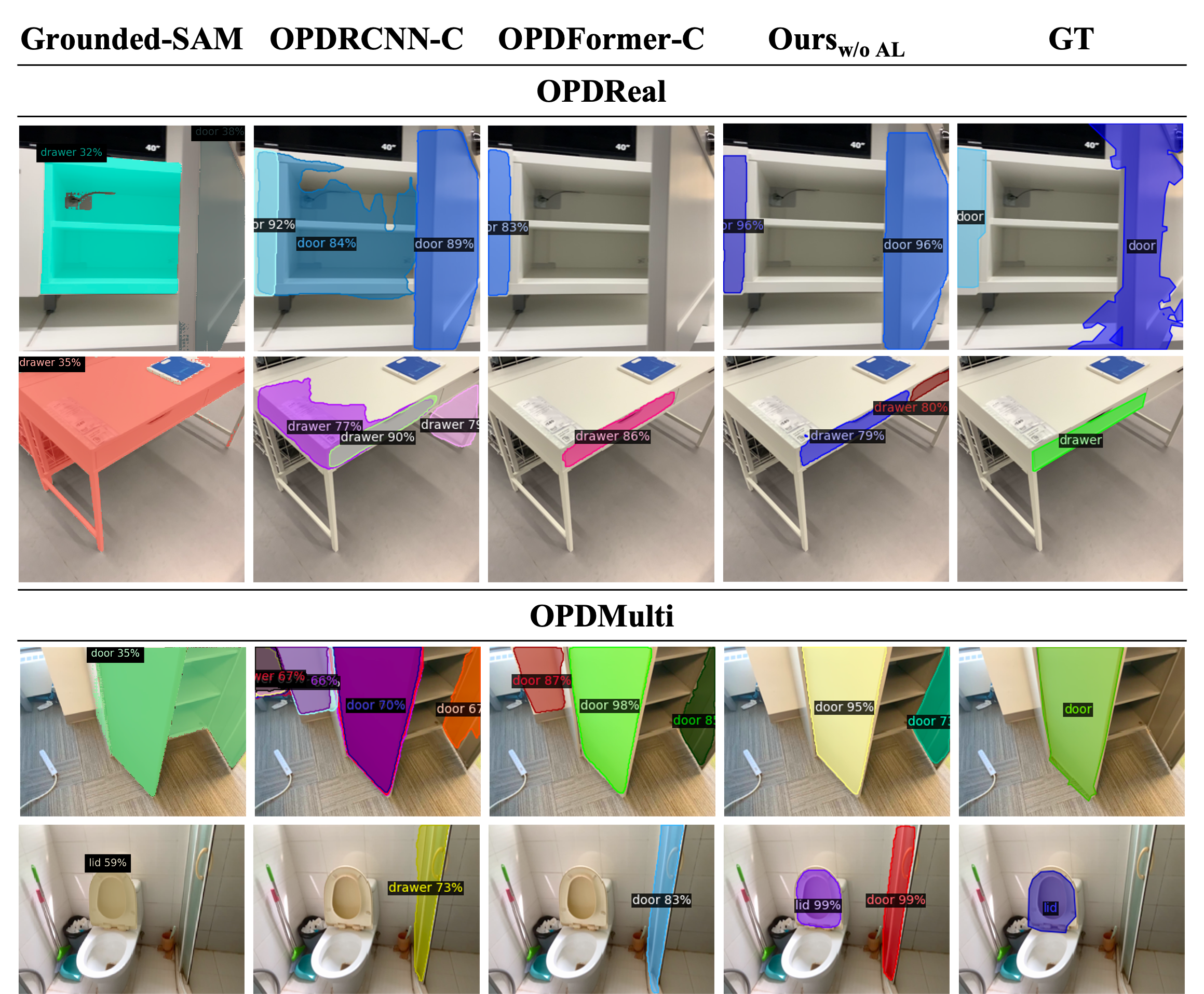
Qualitative results on OPDReal and OPDMulti test set: our method without AL outperforms others on noisy GT (row 1), multiple parts missed in the GT (row 2 & 3) and multiple objects (row 4).

Qualitative results on test set from our dataset: our method outputs better segmentation masks over moveable parts across multiple objects in the image with clear separation of parts and small parts segmentation (row 1 & 3). Our results also show that the coarse-to-fine segmentation framework can effectively reduce segmentation errors from object side surfaces (row 2 & 5).
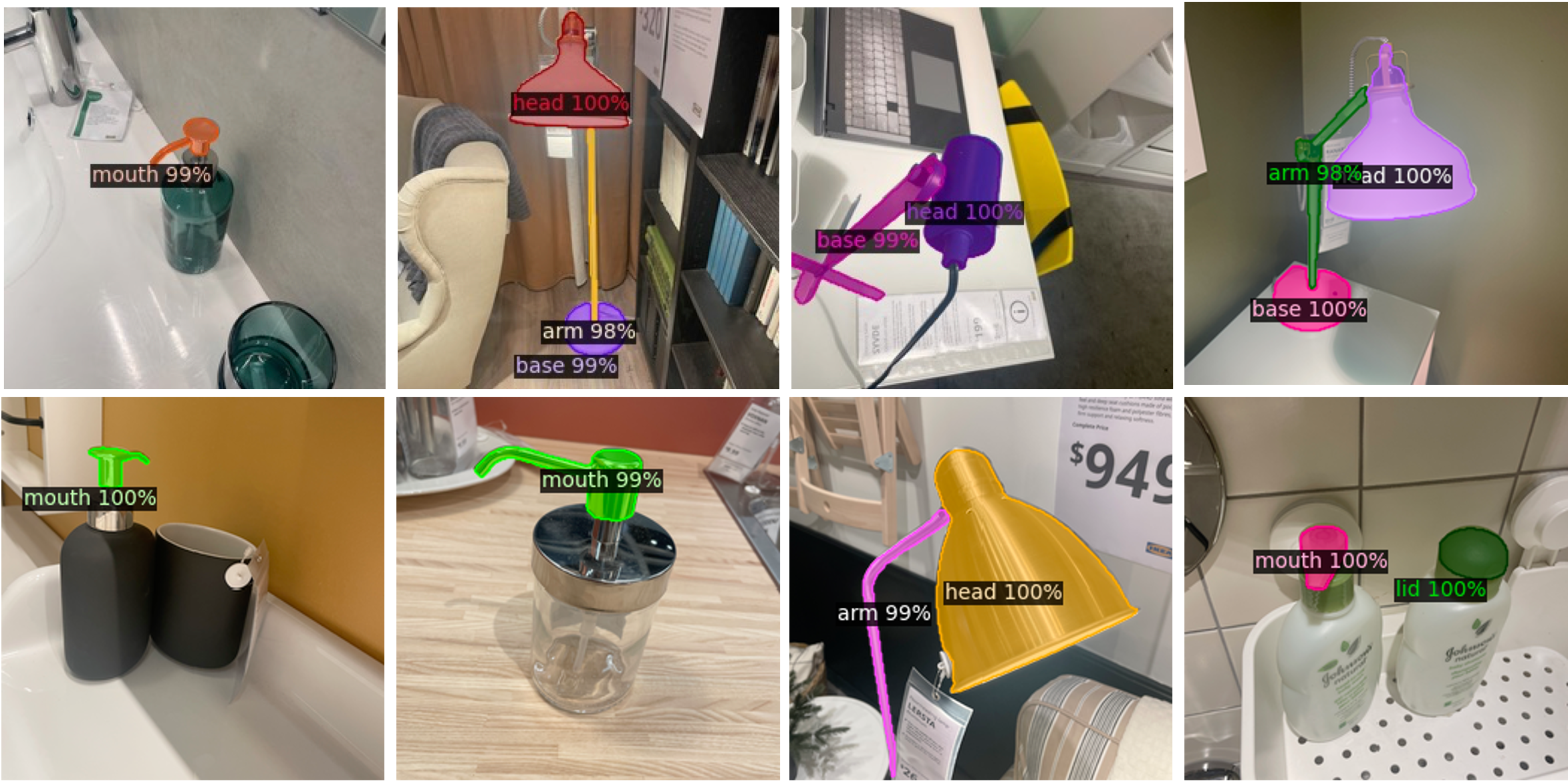

Our model can also generalize on non-openable parts of articulated objects such as lamp and bottle, with a few labeled data (train on 65 images, and inference on 409 images). Results are randomly sampled from the inference.
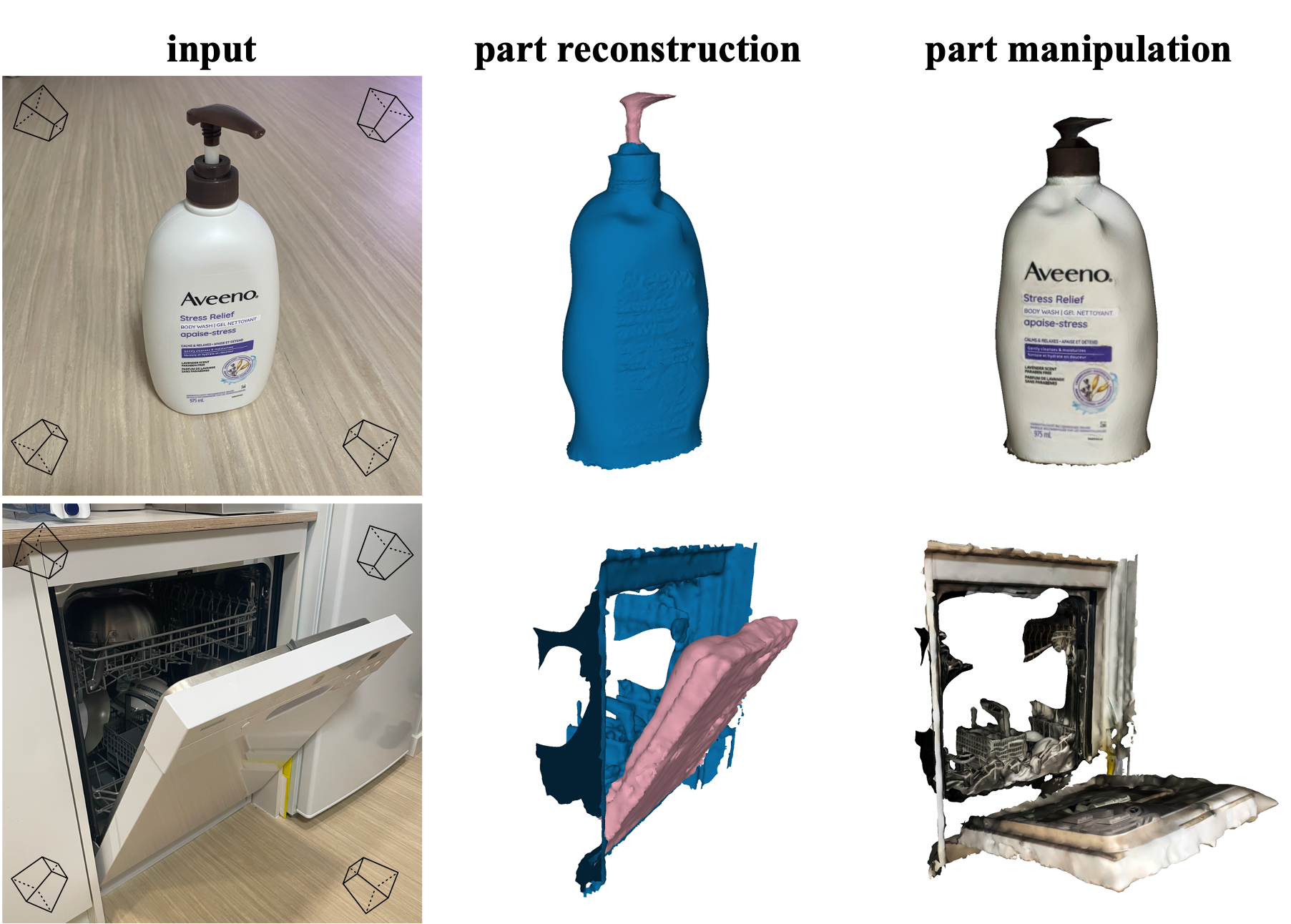

Our work demonstrate practical applications in part based reconstruction and manipulation of articulated objects from images. Given a set of multi-view RGB images of an articulated object, our model predicts precise segmentation masks of moveable parts in each image. This enables part based 3D reconstruction using masked images for both moveable parts and the main body of the object. The resulting 3D models of parts allow for easy manipulation of moveable parts to unseen states in 3D.
@inproceedings{wang2024active,
title={Active Coarse-to-Fine Segmentation of Moveable Parts from Real Images},
author={Wang, Ruiqi and Gadi Patil, Akshay and Yu, Fenggen and Zhang, Hao},
booktitle={European Conference on Computer Vision},
pages={111--127},
year={2024},
organization={Springer}
}